Theme XIII: Vitamins
Vitamins
What are vitamins? Definition, function, characteristics and classification of vitamins. Liposoluble and water-soluble vitamins. Vitamin A. Vitamin B complex (B1, B2, B3, B6, B12, folic acid and Pantothenic acid). Vitamins C, D, E, F and K.
What are vitamins?
Vitamins are a large group of organic compounds involved in various stages of metabolism, benefiting the proper functioning of the whole organism.
The role of vitamins
The basic chemical function of vitamins is to catalyze the organic reactions, participating in the formation of hormones, cells, chemical structures of the nervous system and the composition of
the genetic material.
They combine with the proteins to form enzymes which participate in various body
reactions. Without the presence of vitamins the metabolic processes would be very slow or stopped completely.
This group is very important in fighting all the diseases and for the healthy growth of the organism.
Characteristics and classification of vitamins
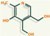
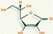
Vitamins can be soluble in fat or water, that effect allows classifying them on liposoluble or water-soluble.
In the first classification are the vitamins A, D, E and K. Due to the ease of their solution in body fat they stored and need not consume daily.
In the water-soluble group are B Complex and Vitamin C that can not be stored since they´re easily removed by body fluids and should be consumed daily preferably, with some exceptions.
The human body does not synthesize vitamins and should be acquired by the daily intake of food, the lack of any of them can cause various diseases.
See details of vitamins:

 Pharmacognosy´s topics - Medicinal plants
Pharmacognosy´s topics - Medicinal plants













Write a comment